To ARDSnet and Beyond
ARDS Mindpalace
Old Definition (published 1994):
Bilateral Infiltrates
PF < 200
"Thought not to be HF" or PCWP < 18
Berlin Definition (new consensus definition 2012)
Respiratory symptoms within ONE WEEK of clinical insult
Bilateral opacities
Respiratory Failure not fully explained by cardiac failure or volume overload. An objective assessment to rule out hydrostatic pulmonary edema is required.
A moderate to severe impairement of oxygenation is present
Mild ARDS: PF 200-300
Moderate ARDS: PF 100-200
Severe ARDS: PF < 100
The Berlin definition did away with the term ALI "Acute Lung Injury" which was previously PF 200-300. It eliminated PCWP from definition as most patients no longer get PA-Caths. Mild ARDS is suggested to be under diagnosed.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Most Common Causes:
Sepsis
Aspiration (Hamman Rich Syndrome)
Pneumonia
Trauma
Massive Transfusion
TRALI
Drug Overdose: ASA, Opioids, Cocaine,
LUNG PROTECTIVE VENTILATION:
Low volume, low pressure ventilation designed to prevent ventilator associated lung injury (VALI/VILI)
Physiology of ards
Histologically in the lungs "diffuse alveolar damage" (DAD) is seen
Initial response to injury: exudative phase, immune cell mediated damage to alveoli
Results in protein rich fluid buildup in the interstitium and alveoli
From there on, inflammatory cytokines are released leading to recruitment of macrophages/T-cells
any injury during this stage is worsened by stretch on alveoli by mechanical ventilation
Second phase is proliferative phase - beginning of healing proess
Edema begins to be reabsorbed, if hte patient survives alveoli regains integrity and function
Third phase: fibrotic phase
Does not occur in all ARDS patients; linked with higher mortality
ARDS Predicted Body Weight Tidal Volume Chart
LITERATURE
ARDSnet: also termed the ARMA trial.
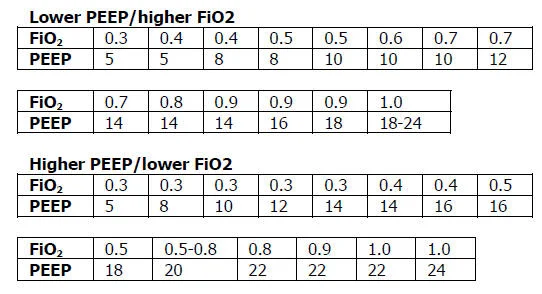
ARDSnet: Compared 6 mL/kg of IBW tidal volume to 12 mL/kg with improvement in mortality. Within the protocol if the patient needed they were allowed to go up to 8 mL/kg which was the highest allowed in the treatment arm. The ARDSnet term when used is what most people refer to the protocol of lung protective strategy with the ARDSnet PEEP/FIO2 table. ARDSnet is a network that produced multiple clinical trials including ARMS, ALVEOLI, and FACTT. It has since changed names to PETAL and still produces ARDS studies.
Low tidal volume will often require "permissive hypercapnea"
ALVEOLI TRIAL
Open Lung Ventilation: refers to the strategy of using PEEP in addition to lung protective strategy to maximize alveolar recruitment. ALVEOLI trial compared low PEEP vs high PEEP in range wtih Fio2 (the table we now all know from ARDSnet). It found no difference in mortality. between using high or low PEEP table.
FACTT TRIAL
FLUID MANAGEMENT: Pulmonary edema is more likely to accumulate in ARDS. Conservative fluid strategy with a target CVP < 4 in ARDS patients. In the ICU this often requires diuresis to keep patient even or negative despite the gtt's they will be recieving.
FACTT: Conservative fluid strategy (targeting CVP < 4) lead to an improvement in oxygenation index, increase in ventilator free days, less days in ICU, and did not increase prevalence of shock. Primary outcome was 60 day mortality which showed no difference.
ACURASYS TRIAL
ACURASYS: Cisatracurium for early ARDS x 48hrs ↓ ’s lung inflammation, overt barotrauma, and mortality
PROSEVA TRIAL
PROSEVA: Proning for at least 16hrs/day in early ARDS ↓’s mortality.
CESAR TRIAL
CESAR Trial: Completed in 2009. Enrolled patients in early 2000's not too far after ARDSnet was published. All patients were shipped to a large quaternary facility from other major tertiary facilities sometimes by Royal Air Force. This was the only center than ran the ECMO arm of this multicenter trial. The other centers kept patients if they were randomized to the control arm. The control arm was allowed to do "usual care" but strongly encouraged to run a low pressure, low volume vent strategy.
Inhaled Vasodilators
Inhaled Nitric Oxide (iNO):
Shown to improve oxygenation but has not been proven to affect mortality. It's affects on oxygenation are also transient.
Inhaled Prostacylcins (iloprost):
Also shown to improve oxygenation without any proven affect in mortality.
Steroids in ARDS
Use if etiology of ARDS is traditionally steroid responsive (Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia for example).
Has been shown to cause harm if used in LATE ARDS (> 14 days)
Could be benefit to use in EARLY ARDS (< 72 hours): Meduri Protocol
Refractory Hypoxemia
GENERAL MANAGEMENT ALGORITHM to REFRACTORY HYPOXEMIA
ARDSnet: proven data
Diuresis (FACTT): proven data
Deepen Sedation (RASS -5)
Paralyze: proven data
PRONE: proven data
VVECMO: proven data
iNO/Iloprost: no proven benefit, expensive but no harm to patient
BiLevel/APRV: no proven benefit, difficult to troubleshoot ventilation issues if you are unfamiliar with mode
To ventilate, cannulate, or osscilate?
Good summary article that came out around the time of PROSEVA, after CESAR and the HFOV articles and reviews all modalities well.
ECMO:
For deeper dive on ECMO; review ECMO podcast by pulmcast (in development) and ECMO high yield users guide.
ELSO guidelines on ECMO in acute respiratory failure
ELSO Position Paper on ECMO in Acute Respiratory Failure
HFOV
HFOV (High Frequency Oscillatory Veniltion): out of favor, previous used as a rescue therapy. It's a type of "open lung recruitment" that basically provides a constant mean airway pressure through very small tidal volumes (1-3 mL/breath) at high frequency (300-900 breaths/min). It was thought to reduce ventilator induced lung injury and was used fairly frequently as a rescue or salvage therapy. Two trials came out in 2013 that ended HFOV as a frequently used therapy in our practice except in very rare occasions. In the era of ECMO and prone positioning there doesn't seem to be much of a role for HFOV.
OSCAR
OSCAR: Targeted moderate to severe ARDS (PF < 200) and used a more conservative strategy in the HFOV arm than OSCILLATE. Lack of standardization in lung protective strategy arm (standard ARDSnet) may have lead to higher mortality in LPV group. No difference in primary end point of 30 day mortality (41%).
OSCILLATE
OSCILLATE: Came out around the same time as OSCAR and utilized a similar patient population (moderate to severe ARDS) but with a higher MAP strategy (up to 38 cm H20) and noted a higher mortality in the HFOV arm. This was felt to be related to maintiaining a higher MAP lead to larger volumes of IVF and pressors for circulatory support.
Attribution
Part 1:
Rock Angel by Joakim Karud https://soundcloud.com/joakimkarud
Creative Commons — Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported— CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/b...
Music promoted by Audio Library https://youtu.be/K8eRXvLL7Wo
"Quizitive" and others by Lee Rosevere is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0 / Songs have been cropped in length from original form
Part 2:
“As Colorful as Ever”, "Something Elated" by Broke For Free is licensed under CC BY-NC 3.0 / Song has been cropped in length from original form